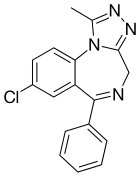
Alprazolam
chemical compound: potent, short-acting anxiolytic of the benzodiazepine class; a minor tranquilizer
Alprazolam, better known by its trade name Xanax, is a short-acting drug. The drug is used to treat people with anxiety disorders and panic attacks.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Alprazolam /ælˈpræzəlæm/ or /ælˈpreɪzəlæm/, Xanax /ˈzænæks/ |
| Trade names | Xanax, Xanor, Niravam, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a684001 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Dependence liability | High |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–90% |
| Protein binding | 80% |
| Metabolism | Liver, via cytochrome P450 3A4 |
| Metabolites | alpha-hydroxyalprazolam, 4-hydroxyalprazolam, beta-hydroxyalprazolam |
| Onset of action | less than an hour[1] |
| Elimination half-life | Immediate release: 4–6 hours Extended release: 11–16 hours |
| Duration of action | 6 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.849 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H13ClN4 |
| Molar mass | 308.77 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Alprazolam is the most commonly misused benzodiazepine (the drug's class) in the United States; but the majority of prescribed users do not develop a substance-use disorder. Alprazolam is a prescription drug in the United States.
References
change- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lilley, Linda Lane; Snyder, Julie S.; Collins, Shelly Rainforth (2016). Pharmacology for Canadian Health Care Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 329. ISBN 9781771720663.