Libra (constellation)
zodiac constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere
Libra (pronounced /ˈliːbrə/, Latin: weighing scale, symbol ![]() , Unicode ♎) is a constellation of the zodiac.
, Unicode ♎) is a constellation of the zodiac.
| Constellation | |
 | |
| Abbreviation | Lib |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Librae |
| Right ascension | 15 |
| Declination | −15 |
| Area | 538 sq. deg. (29th) |
| Main stars | 4, 6 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 46 |
| Stars with planets | 3 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 2 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 2 |
| Brightest star | Zubeneschamali (β Lib) (2.6m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | May Librids |
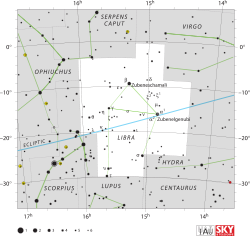
| Bordering constellations | Serpens Caput Virgo Hydra Centaurus (corner) Lupus Scorpius Ophiuchus |
| Visible at latitudes between +65° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of June. | |
It lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east. It once represented the claws of Scorpius.
Some features
changeThe brightest stars in Libra form a rectangle:
- α Librae, Zubenelgenubi ("southern claw"), a visual binary;
- β Librae, Zubeneschamali ("northern claw");
- γ Librae, Zubenelakrab ("scorpion's claw");
- σ Librae, Brachium an eclipsing variable.
α and β Librae are the scales' balance beam, and γ and σ are the weighing pans.
σ Librae was formerly known as γ Scorpii even though it is well inside the boundaries of Libra. It was not renamed as σ Librae until 1851 (by Benjamin A. Gould).