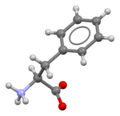
Phenylalanine
chemical compound
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid.
 Skeletal formula of L-phenylalanine
| |||
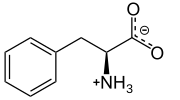 L-Phenylalanine at physiological pH
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | US: /ˌfɛnəlˈæləniːn/, UK: /ˌfiːnaɪl-/ | ||
| IUPAC name
Phenylalanine
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.517 | ||
| |||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 165.19 g·mol−1 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.83 (carboxyl), 9.13 (amino)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
This essential amino acid is neutral and nonpolar. This is because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain.
The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA.
Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and the skin pigment melanin. It is encoded by the codons UUU and UUC.
References
change- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Ihlefeldt, Franziska Stefanie; Pettersen, Fredrik Bjarte; von Bonin, Aidan; Zawadzka, Malgorzata; Görbitz, Prof. Carl Henrik (2014). "The Polymorphs of L-Phenylalanine". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (49): 13600–13604. doi:10.1002/anie.201406886. PMID 25336255.
- ↑ Dawson RM, et al. (1959). Data for Biochemical Research. Oxford: Clarendon Press.