Propene
chemical compound
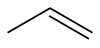
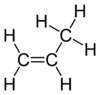
Propene is an organic compound. The substance is also known as propylene and has the formula C3H6. It is the second-simplest alkene. Since it is only made of hydrogen and carbon atoms, it is a hydrocarbon. At room temperature and normal pressure it is a gas.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Propene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.693 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UN number | 1077 In Liquefied petroleum gas: 1075 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 42.08 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.81 kg/m3, gas (1.013 bar, 15 °C) 613.9 kg/m3, liquid | ||
| Melting point | −185.2 °C (−301.4 °F; 88.0 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −47.6 °C (−53.7 °F; 225.6 K) | ||
| 0.61 g/m3 | |||
| Viscosity | 8.34 µPa·s at 16.7 °C | ||
| Structure | |||
| 0.366 D (gas) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| MSDS | External MSDS | ||
| Main hazards | Highly flammable, Asphyxiant | ||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||
| R-phrases | 12 | ||
| S-phrases | 9-16-33 | ||
| Flash point | −108 °C | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Uses
changePropene is produced from fossil fuels, and from coal. Propene is the second most important product used in the petrochemical industry, after ethene. About two thirds are used to produce polypropylene. Propene and benzene are converted to acetone and phenol via the cumene process. Propene is also used to produce isopropanol (propan-2-ol), acrylonitrile, propylene oxide (epoxypropane) and epichlorohydrin.[1]
References
change- ↑ Budavari, Susan, ed. (1996). "8034. Propylene". The Merck Index, Twelfth Edition. New Jersey: Merck & Co. pp. 1348–1349.