Trematode
class of worms
The Trematodes are a class of flatworms in the phylum Platyhelminthes. They are called flukes, and are internal parasites of molluscs and vertebrates. Most trematodes have a complex life cycle with at least two hosts. The primary host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. The intermediate host, which is the agent of dispersal, is usually a snail.
| Trematoda | |
|---|---|
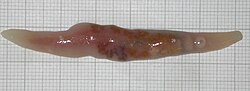
| |
| Botulus microporus, a giant digenean parasite from the intestine of a lancetfish | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | Trematoda Rudolphi, 1808
|
| Subclasses | |
The trematodes or flukes are estimated to include 18,000[1] to 24,000[2] species.
References
change- ↑ Littlewood D.T.J. & Bray R.A. 2000. The Digenea, in Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes. Systematics Association Special Volume #60, pp168–185. ISBN 978-0-7484-0903-7
- ↑ Poulin, Robert; Morand, Serge (17 January 2005). Parasite biodiversity. Smithsonian. p. 216. ISBN 978-1-58834-170-9.