Agonist
An agonist is a type of chemical known as a ligand. It binds to a receptor. It activates (switches on) the receptor to produce a response.
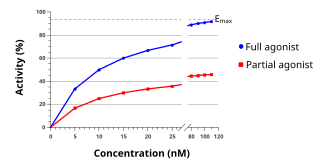
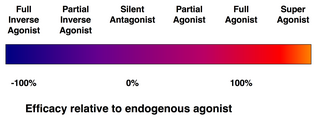
An agonist causes an action. There are also antagonists which block the action of the agonists, and there are inverse agonists which cause an action opposite to that of the agonist.
This is typical of the systems which regulate the body. Being able to control activity is the basis of homeostasis.
Types of agonists
changeReceptors can be activated by either endogenous or exogenous agonists. Both types result in a biological response. Endogenous agonists include hormones and neurotransmitters. Exogenous agonists include drugs.
A substance which causes the same bodily responses, but does not bind to the same receptor is called a physiological agonist.
Examples
change- The endogenous agonist for serotonin receptors is serotonin, and the endogenous agonist for dopamine receptors is dopamine.[1]
- Morphine is an exogenous agonist. It mimics the actions of endorphins at certain receptors in the central nervous system.[2]
References
change- ↑ Goodman and Gilman's Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics. (11th edition, 2008). p14. ISBN 0-07-144343-6
- ↑ they are called μ-opioid receptors