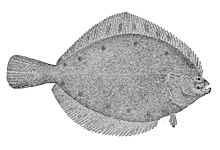
Alaska plaice
Alaska plaice (Pleuronectes quadrituberculatus) are salt water fish that live in the north Pacific Ocean. Like most flatfish, they live on the bottom of the continental shelf, up to 600 metres deep. Their geographical range is from the Gulf of Alaska in the east, to the Chukchi Sea in the north, to the Sea of Japan in the west. Alaska plaice feed mostly on polychaetes, but also eat amphipods and echiurans.
| Alaska plaice | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | P. quadrituberculatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pleuronectes quadrituberculatus Pallas, 1814
| |
Most commercial fisheries do not want to catch Alaska plaice; but many are caught by trawlers trying to catch other bottom fish. So many Alaska plaice get caught anyway that, for example, the 2005 total allowable catch in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands management area (BSAI) was reached before the end of May of that year.
Alaska plaice can live for up to 30 years, and grow to 60 centimetres (24 inches) long, but most that get caught are only seven or eight years old, and about 30 cm (12 in).
Related pages
changeReferences
change- 1998 Marine Fisheries Review article Archived 2007-03-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Bulletin announcing reaching the total allowable catch of Alaska plaice for 2005 (National Marine Fisheries Service)