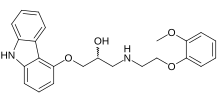
Carvedilol
group of stereoisomers
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. |
Carvedilol is a beta blocker medicine used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and helps prevent heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes.[1] It can also be given with other medicines to treat heart failure and to prevent chest pain caused by angina.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Coreg, others |
| Synonyms | BM-14190 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697042 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 25–35% |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6, CYP2C9) |
| Elimination half-life | 7–10 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (16%), feces (60%) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.117.236 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| (verify) | |
It makes it easier for the heart to pump blood around the body. Usually, carvedilol will need to be taken once or twice a day.[1] It usually starts to work after about 1 hour. But it will take days or weeks for it to reach its full effect.[1]
Related pages
change- Statin drugs
- Lopresor (drug)
- Blood vessel
References
change- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Carvedilol: a medicine used to treat high blood pressure and prevent angina, heart disease and stroke". nhs.uk. 2021-03-11. Retrieved 2024-06-02.