Haplogroup
group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor having the same single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation in all haplotypes
A haplogroup is a group of single chromosomes, or single DNA strands, which share a common ancestor. They have the same mutation in all versions.[1]
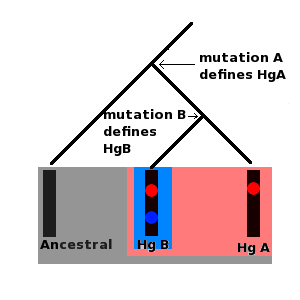
Ancestral Haplogroup
Haplogroup A (Hg A)
Haplogroup B (Hg B)
All of these molecules are part of the ancestral haplogroup. At some time, a mutation occurred in the ancestral molecule, mutation A, which produced a new lineage. This is haplogroup A, defined by mutation A.
Later, a new mutation, mutation B, occurred in a person carrying haplogroup A. Mutation B defined haplogroup B. Haplogroup B is a subgroup of haplogroup A. Both haplogroups A and B are subgroups of the ancestral haplogroup
Haplogroups show deep ancestral origins dating back thousands of years.[2]
In human genetics, the haplogroups usually studied are Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) haplogroups and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups. Both can be used to define genetic populations. Y-DNA is passed only from father to son, while mtDNA is passed only from mother to children. Neither recombines, and thus Y-DNA and mtDNA change only by chance mutations with no intermixture between parents' genetic material.
Related pages
changeReferences
change- ↑ The technical way of saying this is: they have the same single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation in all haplotypes.
- ↑ The International Society of Genetic Genealogy see Haplogroup definition in DNA--NEWBIE GLOSSARY [1]