Methane
Methane is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH
4. It is an alkane with one carbon atom. It is often found as the main part of natural gas. Methane is a greenhouse gas[5][6] 23 times more effective than carbon dioxide. It is also less stable and slowly oxidates by oxygen to carbon dioxide and water.
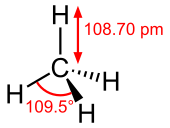
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methane[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Carbane (never recommended[1]) | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 1718732 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.739 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 59 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Methane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UN number | 1971 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH4 | |||
| Molar mass | 16.04 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density |
| ||
| Melting point | −182.5 °C; −296.4 °F; 90.7 K | ||
| Boiling point | −161.50 °C; −258.70 °F; 111.65 K[3] | ||
| 22.7 mg·L−1 | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene, toluene, methanol, acetone and insoluble in water | ||
| log P | 1.09 | ||
| kH | 14 nmol·Pa−1·kg−1 | ||
| Conjugate acid | Methanium | ||
| Conjugate base | Methyl anion | ||
| −12.2×10−6 cm3·mol−1 | |||
| Structure | |||
| Td | |||
| Tetrahedron | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−74.87 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH |
−891.1 to −890.3 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Standard molar entropy S |
186.25 J·(K·mol)−1 | ||
| Specific heat capacity, C | 35.69 J·(K·mol)−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||
| Explosive limits | 4.4–17% | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related {{{label}}} | {{{value}}} | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
It is a gas at 25 degrees Celsius at standard atmosphere (a specific pressure).
Uses
changeMethane is used in gas taps in places such as kitchens, chemistry classrooms, laboratories, etc. as it burns very easily because of its simple molecular structure.
Molecular structure
changeMethane's molecular structure is very simple. It is a single carbon atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms.
Production
changeMethane can be made by many chemical ways, but usually is found in natural gas and is obtained by fractional distillation, after it has become liquid.
References
change- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 3–4. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
Methane is a retained name (see P-12.3) that is preferred to the systematic name 'carbane', a name never recommended to replace methane, but used to derive the names 'carbene' and 'carbyne' for the radicals H2C2• and HC3•, respectively.
- ↑ "Gas Encyclopedia". Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved November 7, 2013.
- ↑ Pubchem. "Methane". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ NOAA Office of Response and Restoration, US GOV. "METHANE". noaa.gov.
- ↑ White House Unveils Plans to Cut Methane Emissions March 28, 2014 New York Times
- ↑ Brad Plumer (December 12, 2016). "Methane levels in the atmosphere are now rising at their fastest pace in decades; It's a big problem for climate change". Vox.com. Retrieved 18 December 2016.


