Midbrain
Brainstem structure that functions as a relay system, transmitting information necessary for vision and hearing. It also plays an important role in motor movement, pain, and the sleep/wake cycle
The mesencephalon or midbrain is a part of the brain stem.[1] It is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.[2]
| Midbrain | |
|---|---|
 Inferior view midbrain (2), above (3) | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | mesencephalon |
| MeSH | D008636 |
| NeuroNames | 462 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1667 |
| TA | A14.1.03.005 |
| FMA | 61993 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
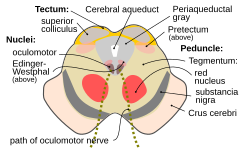
In the anatomy of developing animals, the brain forms from the neural tube, which turns into three vesicles. The mesencephalon (midbrain) is the middle vesicle, and becomes part of the brain stem.
The mesencephalon is ancient in origin, meaning its general architecture is shared with the most ancient of vertebrates. Dopamine produced in the substantia nigra plays a role in motivation and habituation of species from humans to insects.
References
change