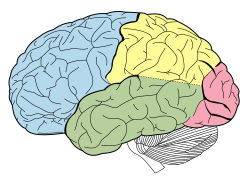
Parietal lobe
part of the brain responsible for sensory input and some language processing
The parietal lobe is a part of the brain positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe.
| Parietal lobe | |
|---|---|
Principal fissures and lobes of the cerebrum viewed laterally. (Parietal lobe is shown in yellow) | |
 Lateral surface of left cerebral hemisphere, viewed from the side. (Parietal lobe is shown in orange.) | |
| Details | |
| Pronunciation | /pəˈraɪ.ə.tl/)[1] |
| Part of | Cerebrum |
| Artery | Anterior cerebral Middle cerebral |
| Vein | Superior sagittal sinus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lobus parietalis |
| MeSH | D010296 |
| NeuroNames | 95 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1148 |
| TA | A14.1.09.123 |
| FMA | 61826 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The parietal lobe brings together information from different senses, particularly spatial sense and navigation. For example, it uses input about touch, balance and the visual system. This enables the parietal cortex to map seen objects in relation to the body (into 'body coordinate positions'). This makes it possible for a person to reach out and handle objects.
The name derives from the overlying parietal bone, which is named from the Latin pariet-, = 'wall'.
References
change- ↑ "PARIETAL - meaning in the Cambridge English Dictionary". dictionary.cambridge.org.