Internal combustion engine
This article does not have any sources. (February 2022) |
An internal combustion engine is an engine in which combustion, or the burning of fuel, occurs on the inside. This differs from external combustion engines where the fire is outside the engine, such as a steam engine.
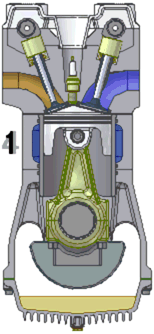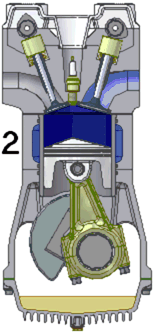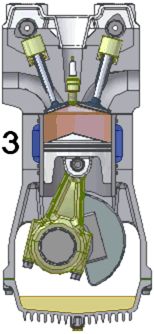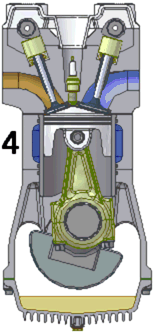
There are many kinds of internal combustion engine but the term often means the machine that Niklaus Otto invented. [source?] In this kind, fire makes pressure increase inside a cylinder. The pressure pushes a piston which is attached to a wheel by a crank. The rod pushes the wheel and makes it spin around. The spinning wheel is attached to other wheels. The engine is very strong and can make all the wheels move.
Engine layouts
changeThere can be many kinds of internal combustion engines such as the single piston engine, the inline engine, the flat engine, the V engine, the VR engine, the W engine, the X engine, the U engine, the H engine, the horizontal K engine, the opposed piston engine, the delta engine, the Wankel or rotary engine and the radial engine which is commonly used in planes.
Common layouts
changeThe most common layouts among these engines are the V layout, and the inline layout. In the V engine, the pistons are aligned in a V shape. There can be V twin engines, with 2 pistons, V3 engines, V4 engines, V6 engines, V8 engines, up to V24 engines. The VR layout is the same as a V layout except the angle between the V shape is smaller making the overall drive smoother. In inline engines, the pistons are aligned in a straight line. There can be inline 1 engines, also called a singular piston engine, all the way up to a straight 14 which was mainly used in older models of cars. Flat engines are the same as inline engines but are aligned horizontally.
W, X, U, H, Horizontal K, Delta and opposed piston engines all have different layouts. In the W engine, the pistons are aligned in a W shape if looked at from the front. The Bugatti Chiron, one of the fastest cars in the world, features a W engine. The pistons in a X are aligned to look like an X from the front. In the U engine, there a 2 inline engine with separate crankshafts and a shared output shaft. When looked at from the front of the engine block, it resembles a U shape. H engines are U engines except there are 2 more inline engines attached to the bottom of the existing inline engines from the U engine. The H and the U layout can be configured vertically or horizontally. In delta engines, the pistons are aligned in a triangle shape. There are 2 pistons per cylinder/combustion chamber, and therefore the minimum amount of pistons in a delta engine is 6. Horizontal K engines have 2 flat pistons facing opposite each other at the bottom and a V engine above them, making them look like a horizontal K. The Opposed piston engines also have 2 pistons per cylinder. They can be aligned vertically or horizontally. When there are only 2 pistons in the engine, they can be called boxer engine.
Radial engines
changeRadial engines are commonly used in planes but are rarely used in cars. An example of this is the Porsche 356 and the 1939 Plymouth Pickup. The pistons in a radial engine are aligned in a star shape. When having multiple sets of pistons, the engines can be stacked beside each other.
Rotary/Wankel engines work the same as a piston engine except they don't have a piston but instead have a rotor that also cycles through the 4 main stages of engines (intake, compression, combustion and exhaust).
Initial startup
changeThere are many different parts to an engine. They include pistons, camshafts, crankshafts, timing belts, and valves. All parts of an engine need to be fully functional for it to work and all parts have a separate role. An engine is usually started by first sending power from the car battery to the ignition coil which then causes an engine spark. The spark then ignites combustion in the cylinders and the combustion starts the engine.
There can be petrol or diesel engines in a vehicle. In petrol or gasoline engines, it is required to have an ignition system to burn the fuel and air mixture. In diesel engines, the ignition system is not required to burn the fuel. Diesel is similar to heating oil. It is burnt through extreme compression.
Mechanics
changeThe car is started using a powerful electric motor, called a starter motor. The starter solenoid converts electrical energy into mechanical energy or movement) and when it starts the ignition switch connects a circuit, sending power to the starter relay. It then sends 2 jolts of electricity into the solenoid, the larger burst directly from the battery pack and the other from the ignition. The magnetic field created from the solenoid connects two metal contact points, one being the solenoid plunger, together which then relays the electricity into the starter motor. The plunger also engages a fork which pushes the pinion gear (connected to the starter motor) to engage the flywheel automatically, starting the engine.
Forced induction and cooling
changeFor extra power, more air is needed to increase the energy evolved per unit of fuel. This is where forced induction must take place. There are some ways of creating forced induction such as turbochargers and superchargers. Turbochargers rely on the volume and velocity of the exhaust to spin the turbine wheel in the middle of the turbocharger. Turbochargers should consume less power from the engine than superchargers and therefore suffer bad throttle response. This delay can also be referred to as turbo lag. Smaller turbochargers spool quickly and deliver more boost pressure at lower engine speeds but suffers at higher RPMs. Bigger turbochargers can deliver more power at higher revs but suffer low throttle response. There can be many turbochargers in a car, but the most common amount being 1 or 2. Superchargers have close to no lag time as the compressor is constantly spinning proportionally to the engine speed. They require torque from the engine to operate. Some common types of superchargers are the Roots-type supercharger, a Screw-type supercharger, and a Centrifugal-type supercharger. In a Roots-type supercharger there are paddles on two drums that are continuously rotating, that force air into the intake. The Roots-type supercharger is a positive displacement device and therefore has the advantage of producing the same pressure ratio at any engine speed. A Screw-type supercharger, like the Roots-type supercharger, is a positive displacement device. They have 2 screws that compress the air and are more efficient than roots type as they create a cooler air output than a roots supercharger but are more difficult to manufacture. A centrifugal-type supercharger, is not a positive displacement device. Although it looks like a turbocharger, they are very different as the power source of the centrifugal supercharger is the engines crankshaft. A turbocharger uses the exhaust gas to spin the compressor.
When using forced induction, the air temperature rises dramatically. To cool the air at higher temperatures, an intercooler is needed. An intercooler cools the air before it enters the cylinder (combustion chamber) using air or water. When hot air enters the combustion chamber, it decreases the fuel efficiency as warm air holds less oxygen than cool air. An air to air intercooler uses the cool air from outside to cool the hot air as it enters the intercooler. The more surface area the intercooler has the cooler the air can get. There are 2 types of air to air intercooler, the bar and plate intercooler and the tube and fin intercooler. Bar and plate intercoolers can cool the air to lower temperature but a tube and fin intercooler cost less and weigh less. In air to water intercoolers, instead of air from outside, it uses a cool liquid to cool the air as it passes though and then uses a radiator to cool the cooling liquid. Air to water intercooler are more complex, heavier and more expensive than air to water intercoolers but can be more efficient.
Transmission
changeCars can also have gears. The gears are controlled by the transmission. They can either be manual, automatic or Continuously Variable Transmission. Gear ratios
Intake and exhaust
changeThe intake manifold is where the car gets the oxygen to burn the fuel
Exhaust in a car is the fumes that come out of the pipe or pipes (normally in back of a car but can be on the sides)
Other information
changeEngines need oil to make them slippery or the moving parts would grind together and stick. Parts of a car engine are measured to 0.01 of a millimetre and some engine parts fit together very tightly.
Most road vehicles use the internal combustion engine, and most of those use the four-stroke engine.
Gas turbines are internal combustion engines that work continuously, not by strokes. Rocket engines and guns are internal combustion engines but they do not turn wheels.
See car battery.