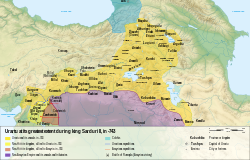
Kingdom of Urartu
Kingdom of Urartu (Assyrian: māt Urarṭu, Babylonian: Urashtu, Hebrew: אֲרָרָט, romanized: Ararat), was an Iron Age kingdom. Territory of the ancient Kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and the Republic of Armenia. Its center was the Armenian highland between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan.[1] During the seventh century, the Urartians collaborated with a combination of Scythians and Cimmerians in their jockeying for power, but by 590, having been weakened in the constant rivalry between Assyrians, Babylonians, Scythians, and Medes, Urartu was swallowed by the Medes.[2]
Urartu and Armenians
changeArmenians are the heirs of the Urartians.[3] A. E. Redgate says that the Urartians are the "most easily identifiable" ancestors of the Armenians.[4] Philip D. Curtin defined the Kingdom of Urartu as an Armenian kingdom.[5]
Maps
change| Map | Year |
|---|---|
| 860–840 BC | |
| 820–785 BC | |
| 785–753 BC | |
| 745–735 BC | |
| 743 BC | |
| 735–715 BC | |
| 713–680 BC | |
| 680–610 BC | |
| 610–585 BC |
References
change- ↑ Kleiss 2008.
- ↑ Jacobson 1995, p. 33.
- ↑ Frye 1984, p. 73.
- ↑ Redgate 2000, p. 5.
- ↑ Curtin 1984, p. 185.
Sources
change- Kleiss, Wolfram (2008). "URARTU IN IRAN". Encyclopædia Iranica.
The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and the Republic of Armenia. Its center was the Armenian highland between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan.
- Jacobson, Esther (1995). The Art of the Scythians: The Interpenetration of Cultures at the Edge of the Hellenic World. BRILL. p. 33. ISBN 90-04-09856-9.
During the seventh century, the Urartians collaborated with a combination of Scythians and Cimmerians¹² in their jockeying for power, but by 590, having been weakened in the constant rivalry between Assyrians, Babylonians, Scythians, and Medes, Urartu was swallowed by the Medes.
- Frye, Richard N (1984). The History of Ancient Iran. Munich: C.H. Beck. pp. 73. ISBN 978-3406093975.
The real heirs of the Urartians, however, were neither the Scythians nor Medes but the Armenians.
- Redgate, A. E (2000). The Armenians. Oxford: Blackwell. pp. 5. ISBN 978-0631220374.
However, the most easily identifiable ancestors of the later Armenian nation are the Urartians.
- Curtin, Philip D. (1984). Cross-Cultural Trade in World History. Cambridge University Press. pp. 185. ISBN 978-0-521-26931-5.
At least three times in history, Armenians rose to unusual territorial power. The first was in the ninth to the sixth century B.C., where the Armenian kingdom of Urartu was an important stopping point for trade between Asia and the Mediterranean world.