Asparagine
group of stereoisomers
Asparagine is an non-essential amino acid. Our bodies can make it. It is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
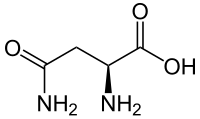 Skeletal formula of L-asparagine
| |||

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Asparagine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.565 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8N2O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 132.12 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white crystals | ||
| Density | 1.543 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 234 °C (453 °F; 507 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 438 °C (820 °F; 711 K) | ||
| 2.94 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in acids, bases, negligible in methanol, ethanol, ether, benzene | ||
| log P | −3.82 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| -69.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| orthorhombic | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−789.4 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
References
change- ↑ Haynes WM, ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.


