Judah
Southern Israelite kingdom, c. 930–586 BCE
The Kingdom of Judah was an ancient Israelite kingdom that existed in the southern part of the Levant. It was on the western shore of the Dead Sea. Its main cities were Jerusalem and Hebron. It existed from the 9th[1][2] or 8th century BC,[3] up until 586 BC.
Kingdom of Judah 𐤉𐤄𐤃 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9th or 8th century BCE–586 BCE | |||||||||
|
LMLK (of the king) national seal dated 700-586 BCE. | |||||||||
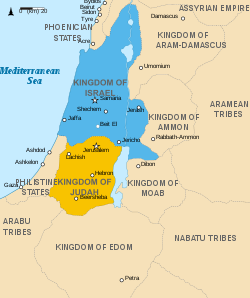 Judah and surrounding states in the 9th century BCE | |||||||||
| Capital | Hebron Jerusalem | ||||||||
| Common languages | Hebrew | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Judahite, Israelite | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Historical era | Levantine Iron Age | ||||||||
• Jeroboam's Revolt | 9th or 8th century BCE | ||||||||
• Siege of Jerusalem (587 BCE) | 586 BCE | ||||||||
| |||||||||
After the death of Saul, Israel picked David to rule them. (1 Chronicles 11:1) After the death of King Solomon, son of David, ten of the twelve of the tribes of Israel did not want Solomon's son, Rehoboam to lead them. This caused the kingdom to split the Northern Kingdom, the Kingdom of Israel and the Southern Kingdom, the Kingdom of Judah. Jerusalem was the capital of the Kingdom of Judah.
In 586 BC, the king of Babylon, Nebuchadnezzar II, took over Jerusalem and destroyed Judah.
References
change- ↑ Lester L. Grabbe, ed. (2008). Israel in Transition: From Late Bronze II to Iron IIa (c. 1250–850 B.C.E.). T&T Clark International. pp. 225–6. ISBN 978-0567027269.
- ↑ Lehman in Jerusalem in Bible and Archaeology: The First Temple Period. Sheffield. 1992. p. 149. ISBN 9781589830660.
- ↑ Finkelstein, Israel (2006). "The Last Labayu: King Saul and the Expansion of the First North Israelite Territorial Entity". In Amit, Yairah; Ben Zvi, Ehud; Finkelstein, Israel; et al. (eds.). Essays on Ancient Israel in Its Near Eastern Context: A Tribute to Nadav Naʼaman. Eisenbrauns. pp. 171 ff. ISBN 9781575061283.
