Omega-3 fatty acid
fatty acids with a double bond (C=C) at the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain
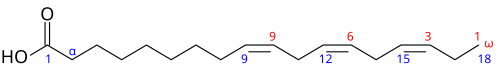
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids. They have a double bond three atoms away from the end methyl group.
The most common sources for plant oils are walnuts, hemp oil and flaxseed oil. Sources of animal omega-3 fats include eggs, squid oils and fish.
Dietary supplementation does not affect the risk of cancer, heart disease or death.[1]
They are not a main treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism and other developmental disabilities. However, omega-3 supplements are often given to children with these conditions.[2]
References
change- ↑ "Omega-3 Fatty Acids". The National Institutes of Health. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Levy, Susan E.; Hyman, Susan L. (2005). "Novel Treatment for Autistic Spectrum Disorders". Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 11 (2). Wiley Online: 131–142. doi:10.1002/mrdd.20062. PMID 15977319. Retrieved May 14, 2021.