Iraq
Iraq is a country in southwestern Asia. Iraq borders with Saudi Arabia and Kuwait to the south, Turkey to the north, Syria to the north-west, Jordan to the west, and Iran to the east. The capital of Iraq is Baghdad.
Republic of Iraq | |
|---|---|
| Motto: الله أكبر (Arabic) "Allahu Akbar" (transliteration) "God is the Greatest" | |
| Anthem: "Mawtini" "موطني" (English: "My Homeland") | |
 | |
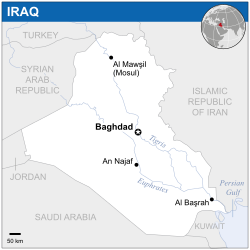 | |
| Capital and largest city | Baghdad 33°20′N 44°26′E / 33.333°N 44.433°E |
| Official languages | |
| Religion | Islam |
| Demonym(s) | Iraqi |
| Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Latif Rashid | |
| Mohammed Al Sudani | |
| Mohamed al-Halbousi | |
| Medhat al-Mahmoud | |
| Legislature | Council of Representatives |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
• Kingdom | 3 October 1932 |
| 14 July 1958 | |
| 15 October 2005 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 437,072 km2 (168,754 sq mi) (58th) |
• Water (%) | 1.1 |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 43,533,592[1][2] (36th) |
• Density | 82.7/km2 (214.2/sq mi) (125th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $695 billion[3] (34th) |
• Per capita | $17,429[3] (71st) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $223 billion[3] (47th) |
• Per capita | $5,601[3] (88th) |
| Gini (2012) | 29.5[4] low |
| HDI (2017) | medium · 120th |
| Currency | Iraqi dinar (IQD) |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (AST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +964 |
| ISO 3166 code | IQ |
| Internet TLD | .iq |
| |
Iraq has been known by the Greek name Mesopotamia which means (Land between the rivers) and has been home to continuous successive civilizations since the 6th millennium BC. The region between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers is often referred to as the cradle of civilization and the birthplace of writing. Iraq was part of several empires, some were Safavid, and Afsharid. During the Mesopotamian Campaign of World War I, British Empire troops conquered the Ottoman Empire provinces of Basra and Baghdad and later added the province of Mosul to make Iraq.
Most Iraqis are Shia Muslim with a significant Sunni Muslim minority.
Politics
changeFrom 1968 to 2003, Iraq was run by the Ba'ath Party. Saddam Hussein was the President from 1979 until the disbandment of the Ba'ath Party.
After the 1990 invasion of Kuwait many countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Saudi Arabia, France, Italy, Pakistan, and others fought to free Kuwait. Later, some agents believed to be sent by Saddam Hussein tried to kill former President George H. W. Bush with a truck bomb in Kuwait.
The Kurdistan Region gained autonomy in the 1990s. Kurdistan region has its own parliament.
The March 2003 invasion of Iraq was led by American, British, Australian, Danish and Polish forces. They forced the Ba'ath Party to surrender. The publicly stated reason for the invasion was that Saddam Hussein refused to let United Nations inspectors look for suspected nuclear, biological, and chemical weapons. In the past, Saddam Hussein used chemical weapons to kill the Kurds. Iraq had done research in making biological and nuclear weapons.
The country was initially split into 3 zones, the American zone, the British zone, and the Polish zone similar to the way Germany was divided in 1945. Forces from Denmark controlled areas in the British zone. A new temporary government was formed on June 28, 2004. The coalition forces were in the country.
There were many U.S., British and multi-national troops in the country until December 15, 2011 when the Iraq War had ended. Tensions between religious groups (Shia and Sunni Muslims, as well as Christians) lead to a great deal of instability in the country.
Geography
changeThe country area lies between two rivers; for this reason the area was called Mesopotamia in ancient ages. The rivers Euphrates and Tigris bound what is called the Fertile Crescent. Iraq also has a small coastline along the Persian Gulf, and this coastline was considered the heart of the petroleum trade in Iraq before the First Gulf War. The weather is extremely hot and dry because Iraq is far from seas and oceans and even the close ones are blocked by mountains so that the rainy wind can not reach the inlands. This region has fertile land because of the two rivers.
Iraq is divided into 18(discluding partially recognized halabja)Governorates (muhafazah). also the Iraqi Constitution has recognized only one autonomous federal region inside Iraq, the name of the region is Kurdistan Region, this region consists of the three Governorates(and one partially recognized one)of Duhok ( دهوك ), Erbil ( اربيل ), As-Sulaymaniyah (السليمانية ) and Halabja (حلبجة)
Kurdistan Region Governorates are marked in bold.
Partially recognized Governorate are marked in Italic.
Economy
changeIraq has a large amount of oil. Iraq is the world's number four in petroleum production and the world's number two in petroleum reserves. In the past, Iraq sold much of this oil to other countries. After Iraq invaded Kuwait in August 1990, the United Nations stopped Iraq from selling the oil. The United Nations later allowed Iraq to sell some oil to buy food, clothes, and medicine so the people would not suffer as much. This was called the "Oil-for-Food" program.
Related pages
changeReferences
change- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022". population.un.org. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX). population.un.org ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved July 17, 2022.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Iraq". International Monetary Fund.
- ↑ "World Bank GINI index". Data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2016-08-17.
- ↑ "2018 Human Development Report" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2015. p. 9. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
Other websites
changeMedia related to Iraq at Wikimedia Commons

