Georgia (country)
42°00′N 43°30′E / 42.000°N 43.500°E
Georgia | |
|---|---|
| Motto: ძალა ერთობაშია Dzala ertobashia "Strength is in Unity" | |
| Anthem: თავისუფლება Tavisupleba "Freedom" | |
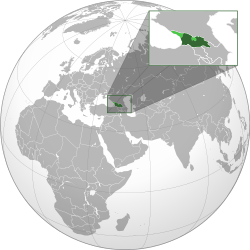 Georgian territory under central control in dark green; uncontrolled territory in light green | |
| Capital and largest city | Tbilisi 41°43′N 44°47′E / 41.717°N 44.783°E |
| Official languages | Georgian Abkhaz[1][2] |
| Ethnic groups (2014[a]) |
|
| Religion (2014) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Georgian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
• President of Georgia | Salome Zourabichvili |
• Prime Minister of Georgia | Irakli Kobakhidze |
• Chairperson of the Parliament of Georgia | Shalva Papuashvili |
| Legislature | Parliament of Georgia |
| Establishment | |
• Colchis and Kingdom of Iberia | 13th c. BC – 580 AD |
• Kingdom of Abkhazia and Kingdom of the Iberians | 786–1008 |
• Unification of the Georgian realm | 1008 |
• Triarchy and collapse of the Kingdom of Georgia | 1463–1810 |
• Georgia within the Russian Empire | 12 September 1801 |
• Democratic Republic of Georgia | 26 May 1918 |
• Red Army invasion of Georgia | 25 February 1921 |
• Independence from the Soviet Union • Declared • Finalized | 9 April 1991 25 December 1991 |
• Current constitution | 24 August 1995 |
| Area | |
• Total | 69,700 km2 (26,900 sq mi) (119th) |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | 4,012,104[b] (128th) |
• 2014 census | |
• Density | 57.6/km2 (149.2/sq mi) (137th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2019) | very high · 61st |
| Currency | Georgian lari (₾) (GEL) |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (Georgia Time GET) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +995 |
| ISO 3166 code | GE |
| Internet TLD | .ge, .გე |
Website www | |
| |
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is situated on the coast of the Black Sea and borders Russia to the north, Turkey and Armenia to the south, and Azerbaijan to the southeast. It is largely encircled by the Greater and Lesser Caucasus mountain ranges.[source?]
During 1918–1921, and 1991–1995 its full name was the Republic of Georgia. Since 1995 it is Georgia, as written in her constitution. It was part of the Russian Empire and later Soviet Union between 1921 and 1991, but now it is an independent republic. The capital city is Tbilisi. Almost 4 million people live there.[source?]
History
changeBefore 15th century
changeThe Georgians have existed as a nation since classical antiquity. Their capital Tbilisi, formerly named Tiflis, was founded in the 5th century, by King Vakhtang I of Iberia. Back then, western Georgia was colonized by the Roman Empire.[10] The Arabs conquered it in 635 AD. Despite centuries of Islamization, the Georgian culture flourished via trade. In the 10th century, Arab influence diminished in the Caucasus.[source?] In 1008, the Kingdom of Georgia was formed. It was a major country in the region until the Mongol Empire invaded it in 1223. Georgia was part of the Mongol Empire for a century on and off until 1334, when King Giorgi V took over.[source?]
Early modern period
changeIn the 1400s, Georgia dissolved into several principalities. In the 1500s the Persians invaded eastern Georgia four times from 1541 to 1544. In 1555 the Kings of Kartli ruled through the will of the Persian Shahs (kings of a Persian empire).[11]
Modern period
changeIn 1783, the treaty of Georgievsk was signed between Catherine the Great of Russia and King Heraclius II, giving Russia the power to protect Georgia. Then, in 1798 the Persians burned Tbilisi to the ground. From 1811 to 1918, Georgia was under the Tsar of Russia. Their culture survived intact. From 1918 to 1921, Georgia was independent, but then conquered by the Soviet Union (USSR) and colonized, briefly interrupted by Nazi occupation in WWII, until the end of the USSR in December 1991.[11]
Post-Soviet period: 1990s
changeIn 1991, most Georgians voted to restore their sovereignty as a free nation. They then declared their independence. However, the re-established Republic of Georgia saw a bloody civil War that led to the downfall of first-ever president of Georgia Zviad Gamsakhurdia. Georgia was also involved in War in Abkhazia between 1992 and 1993. They went through a rough patch between 1994 and 1995 when the economy underperformed, despite significant improvements in final years of the 20th century.[source?]
Post-Soviet period: 21st century
changeSince the 2000s, Georgia has been applying for EU and NATO membership. In 2008, Georgia was illegally invaded by Russia and lost 20% of her territory, with Abkhazia and South Ossetia having fallen under Russian occupation ever since.[11][12]
2024 – present
changeSince 26 October 2024, the ruling party Georgian Dream (GD), beset with allegations of corruption and pro-Russian authoritarianism,[13] has been accused of rigging the Georgian parliamentary election run on that day. The crisis came to a head when the GD government announced the postponement of EU membership talks until 2028,[14] setting off an intense wave of pro-democracy protests[15][16] unseen since the 2003 Rose Revolution.[17] Of Georgia's 3.76 million population in 2024, over 100,000 have participated in at least eight Georgian cities.[18][19]
Geography
changeGeorgia is located next to the countries of Russia, Turkey, Armenia and Azerbaijan. It has a coastline along the Black Sea. It is located at the edge of Europe and Asia. Georgia has many mountains, whose highest point is 5,193 m above sea level. The mountains running through Georgia are called the Caucasus Mountains. The highest mountain in Georgia is Mount Shkhara at 5,193 m. The coastline of Georgia is 310 km long. Georgia has about 25,000 rivers. The largest river is the Mtkvari.[source?]
Divisions
changeGeorgia is divided into 9 regions, 1 city, and 2 autonomous republics. These in turn are divided into 67 districts and 12 self-governing cities.[20]
The region of Abkhazia declared independence in 1999.[21] South Ossetia is officially known by Georgia as the Tskinvali region. Georgia considers both regions as occupied by Russia.[22]
| Region | Centre | Area (km2) | Population[5] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhazia | Sokhumi | 8,660 | 242,862est | 28.04 |
| Adjara | Batumi | 2,880 | 333,953 | 115.95 |
| Guria | Ozurgeti | 2,033 | 113,350 | 55.75 |
| Imereti | Kutaisi | 6,475 | 533,906 | 82.45 |
| Kakheti | Telavi | 11,311 | 318,583 | 28.16 |
| Kvemo Kartli | Rustavi | 6,072 | 423,986 | 69.82 |
| Mtskheta-Mtianeti | Mtskheta | 6,786 | 94,573 | 13.93 |
| Racha-Lechkhumi and Kvemo Svaneti | Ambrolauri | 4,990 | 32,089 | 6.43 |
| Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti | Zugdidi | 7,440 | 330,761 | 44.45 |
| Samtskhe-Javakheti | Akhaltsikhe | 6,413 | 160,504 | 25.02 |
| Shida Kartli | Gori | 5,729 | 300,382est | 52.43 |
| Tbilisi | Tbilisi | 720 | 1,108,717 | 1,539.88 |
Culture
changeAbout 4 million people live in Georgia. About 1.2 million live in Tbilisi.[source?] People from Georgia are called Georgians, most of whom speak Georgian as their first language, though some speak Azerbaijani, Armenian, Russian or other languages as well. Georgians use three alphabets, namely the Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri and Mkhedruli, with Asomtavruli being the very first Georgian alphabet, which was said to be invented by King Pharnavaz I of Iberia.[source?] The most famous person to have come from Georgia is Josef Stalin, Soviet Union's totalitarian communist dictator between 1922 and 1953.[23][24] Most Georgians are Orthodox Christians, but there are Jews[25] and Muslims as well due to partial Arab colonization in the Middle Ages.[26] The currency of Georgia is the lari.[27]
Related pages
changeReferences
change- ↑ "Article 8", Constitution of Georgia. In the Abkhazian Autonomous Republic (Abkhazian AR), also Abkhazian.
- ↑ "Constitution of Georgia" (PDF). Parliament of Georgia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 December 2017.
- ↑ "საქართველოს მოსახლეობის საყოველთაო აღწერის საბოლოო შედეგები" (PDF). National Statistics Office of Georgia. 28 April 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- ↑ "Demographic Portal". Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "2014 General Population Census Main Results General Information — National Statistics Office of Georgia" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2021". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 6 March 2022.
- ↑ "GINI index (World Bank estimate) - Georgia". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Archived from the original on 20 July 2018. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ↑ "Human Development Report 2020" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 15 December 2020. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- ↑ "Living conditions". GeoStat. Archived from the original on 3 February 2017. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑
- Gamqreliże, Gela (2014). "Archaeology Of The Roman Period Of Georgia". NYU | Faculty Digital Archive. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Rapp Jr., Stephen H. (29 March 2017). "Georgia before the Mongols". Oxford Research Encyclopedias. doi:10.1093/acrefore/9780190277727.013.282. ISBN 978-0-19-027772-7. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Aleksidze, Nikoloz; Baker-Brian, Nicholas J.; Lössl, Josef (20 April 2018). "Caucasia: Albania, Armenia, and Georgia". A Companion to Religion in Late Antiquity. Wiley Online Library. doi:10.1002/9781118968130.ch7. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Vacca, Alison (2020). "3. Buldān al-Rān: the many definitions of Caucasian Albania in the early Abbasid period". From Albania to Arrān. Gorgias Press. pp. 37–84. doi:10.31826/9781463239893-007. ISBN 978-1-4632-3989-3. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Wier, Thomas R. (24 May 2024). "Caucasian Albania: An International Handbook". Caucasus Survey. Brill. pp. 1–6. doi:10.30965/23761202-bja10038. ISSN 2376-1199. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2
- Rayfield, Donald (11 February 2019). Edge of Empires: A History of Georgia. Reaktion. ISBN 9781789140590. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Gamkrelidze, Irakli; Okrostsvaridze, Avtandil; Koiava, Kakhaber; Maisadze, Ferando (2021). "Overview of the History and Culture of Georgia". Geotourism Potential of Georgia, the Caucasus. Geoheritage, Geoparks and Geotourism. pp. 1–10. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-62966-3. ISBN 978-3-030-62965-6. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- The History of Georgia: Mysteries of the Caucasus - Softcover. 2023. ISBN 9798396381513. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia country profile - BBC News". BBC News. 28 October 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia". Britannica. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Also known as: Sakartvelo, Sakartvelos Respublika
- ↑
- Gordadze, Thornike (2011). "Georgia-Russia Conflict in August 2008: War as a Continuation of Politics". Reassessing Security in the South Caucasus (1 ed.). Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781315603872-3 (inactive 12 December 2024). ISBN 9781315603872. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of December 2024 (link) - Cappucci, M. (November 2013). "Making an European country in the Caucasus: The Georgian experience" (PDF). Revista Română de Geografie Politică: 113–128. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Kitaevich, Evgenia Jane (2 May 2014). "History that splinters: education reforms and memory politics in the Republic of Georgia". Political Transformation and Social Change in the South Caucasus. Vol. 14. pp. 319–338. doi:10.1080/14683857.2014.906089. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Lanoszka, Alexander (18 December 2017). "Tangled up in rose? Theories of alliance entrapment and the 2008 Russo-Georgian War". Contemporary Security Policy. 39 (2): 234–257. doi:10.1080/13523260.2017.1392102. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "16th Anniversary of Russia-Georgia 2008 War -International Reactions". Civil Georgia. 7 August 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Gordadze, Thornike (2011). "Georgia-Russia Conflict in August 2008: War as a Continuation of Politics". Reassessing Security in the South Caucasus (1 ed.). Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781315603872-3 (inactive 12 December 2024). ISBN 9781315603872. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑
- "Is the Kremlin behind Georgia's foreign agents law?". Chatham House. 23 May 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Georgia has been captured by a tiny elite [...] by Russia.
- "Georgian Ruling Party's Parliamentary Picks Show Russian Drift, Critics Say". Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP). 11 September 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Georgia's ruling party has chosen the controversial billionaire Bidzina Ivanishvili as its top candidate for next month's parliamentary elections – a decision critics said was the latest sign of the party's drift towards Russian-style authoritarianism.
- "Pro-Russian Georgian Dream holds onto power". Le Monde. 27 October 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
The electoral commission announced on Sunday morning that Georgian Dream had won with 54% of the vote, despite protests from opposition parties. This will enable billionaire Bidzina Ivanishvili to form a government, but risks dashing the country's hopes of joining the European Union.
- "Georgian Dream or Democratic Nightmare? The Struggle for Democracy Amid Voter Fraud and Russian Interference". The Soufan Center. 30 October 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Accused of interference in Georgia, Russia pumps up anti-US propaganda". Voice of America (VOA). 31 October 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Georgian opposition supporters rally to protest results of the parliamentary elections that showed a win for the ruling Georgian Dream party [...] Oct. 28, 2024.
- "Is the Kremlin behind Georgia's foreign agents law?". Chatham House. 23 May 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑ "Statement on Georgia's Suspension of European Union Accession". U.S. Department of State. 30 November 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑
- "At Georgian Protests, Journalists Say They're Being Targeted And Beaten". Radio Liberty. 30 November 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Giordano, Elena (30 November 2024). "Georgia protests escalate, demonstrators clash with police after EU talks halted". Politico. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Thousands of protesters rallied in Tbilisi for a second night over the government's decision to suspend EU membership negotiations.
- "Protests erupt across Georgia in defiance of government's anti-EU stance". The Kyiv Independent. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia protests enter fourth night as opposition grows to freeze on EU talks". The Guardian. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Georgian media reports protests in at least eight cities and towns after Saturday's demonstrations leave 44 in hospital.
- "Police and Protesters Clash in Georgian Capital". The New York Times. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
The government's decision to suspend its bid for European Union membership has driven thousands of protesters into the streets.
- ↑
- "Over 40 people hospitalized in Georgia during protests over suspension of EU talks". NPR. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia's battle for Europe: Protesters defy government's stance - VIDEO". News.Az. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Protests in Georgia spread as PM defies US condemnation". Reuters. 2 December 2024.
- "Live Blog: Aborted EU Accession | Riot Police Begin Dispersing Protesters". Civil Georgia. 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia: Mass protests grow entering fourth night". DW News. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Tens of thousands of Georgians continue to pressure the government over EU accession as opposition figures cry fraud. President Salome Zurabishvili has said she won't step down and is calling for a new vote.
- ↑
- Kandelaki, Giorgi (1 July 2006). "Georgia's Rose Revolution: A Participant's Perspective". United States Institute of Peace (USIP). Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Papava, Vladimer (22 August 2006). "The Political Economy of Georgia's Rose Revolution". Orbis (East European Democratization). 50 (4). Elsevier: 657–667. doi:10.1016/j.orbis.2006.07.006. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Welt, Cory (5 June 2012). "Chapter 7 - Georgia's Rose Revolution From Regime Weakness to Regime Collapse". Democracy and Authoritarianism in the Postcommunist World. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "She Coined The Catchphrase: Looking Back On The 'Rose Revolution'". Radio Liberty. 23 November 2018. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Georgia: The thorns of the Rose Revolution". DW News. 22 November 2023. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Twenty years after a non-violent change of power in the post-Soviet state of Georgia, the legacy of the Rose Revolution remains a source of debate. The country is still trying to position itself politically.
- "Twenty Years Since Rose Revolution of 2003: Gains, Losses and Lessons". Civil Georgia. 23 November 2023. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑
- "VIDEO | Protests in Georgia over the government's decision to suspend talks with EU". Baltic News Network. 29 November 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "UPDATE: Fourth night of pro-EU protests sweep streets of Georgia's capital". TVP World. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Landsbergis: Baltic States Agreed to Impose Sanctions on Those Who Undermine Democracy in Georgia". Civil Georgia. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Riot police clear parliament zone; protesters remain on Rustaveli avenue, facing off water cannons". Georgia Today. 2 December 2024.
- "Zurabishvili calls for action on constitutional court inactivity". Georgia Today. 2 December 2024.
- ↑
- "Mayhem in Georgia as protesters armed with home-made MACHINE GUN blasts riot police with fireworks: Chaos deepens as pro-EU campaigners and cops clash in fiery street battles, with over 100 arrested". Daily Mail. 30 November 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- "Watch: Anti-Russia protesters turn 'fireworks gun' on riot police in Georgia". The Telegraph. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Third night of violence in capital Tbilisi after government delays EU membership talks amid wider post-election crisis
- "Georgia: Demonstrators launch fireworks against riot police in Tbilisi protests". Sky News. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Protesters used fireworks against riot police in Tbilisi on the third night of demonstrations against the government's decision to suspend negotiations to join the European Union.
- "Moment anti-Russian protestors shoot fireworks gun at police in angry scenes". Daily Express. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Thousands have been arrested in ongoing clashes in the Georgian capital Tbilisi, between police and anti-Russian protesters.
- "Protester shoots 'fireworks gun' at riot police during pro-EU protests in Georgia". The Independent. 1 December 2024. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑ "Registry of Municipalities". National Agency of Public Registry. Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- ↑ "Regions and territories: Abkhazia". BBC News. 8 February 2011. Archived from the original on 20 April 2010. Retrieved 30 January 2011.
- ↑ Abkhazia, S. Ossetia Formally Declared Occupied Territory. Archived 3 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine Civil Georgia. 28 August 2008.
- ↑
- Conquest, Robert (1968). The Great Terror: Stalin's Purge of the Thirties. Bodley Head. ISBN 9781847925688. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Gellately, Robert 2007. Lenin, Stalin, and Hitler: the age of social catastrophe. Knopf. ISBN 978-1-4000-4005-6.
- Figes, Orlando 2007. The Whisperers: private life in Stalin's Russia. London: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-7139-9702-6.
- Wheatcroft, Stephen G. (1999). "Victims of Stalinism and the Soviet Secret Police: the comparability and reliability of the archival data: not the last word" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 51 (2): 339. doi:10.1080/09668139999056.
- Ellman, Michael (2002). "Soviet Repression Statistics: some comments" (PDF). Europe-Asia Studies. 54 (7): 1151–1172. doi:10.1080/0966813022000017177. S2CID 43510161.
The best estimate that can currently be made of the number of repression deaths in 1937–38 is the range 950,000–1.2 million, i.e. about a million.
- ↑
- Bezo, Brent; Maggi, Stefania (15 April 2015). "Living in "survival mode:" Intergenerational transmission of trauma from the Holodomor genocide of 1932–1933 in Ukraine". Social Science & Medicine. 134: 87–94. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.04.009. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- Andriewsky, Olga (2015). "Towards a decentred history: The study of the Holodomor and Ukrainian historiography". East/West: Journal of Ukrainian Studies. 2 (1): 17. doi:10.21226/T2301N. ISSN 2292-7956. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- Boriak, Hennadii (2008). "Population Losses in the Holodomor and the Destruction of Related Archives: New Archival Evidence". Harvard Ukrainian Studies. 30 (1/4). Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute: 199–215. JSTOR 23611473.
- "Worldwide Recognition of the Holodomor as Genocide". Holodomor Museum. 24 November 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- "Holodomor | Holocaust and Genocide Studies | College of Liberal Arts". University of Minnesota Twin Cities. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- Mills, Claire; Walker, Nigel (3 March 2023). "Ukrainian Holodomor and the war in Ukraine". House of Commons Library. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- ↑
- Gitelman, Zvi (1991). "Ethnic identity and ethnic relations among the Jews of the non-European USSR". Ethnic and Racial Studies. 14 (1: National identity in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union): 24–54. doi:10.1080/01419870.1991.9993697. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
Published online: 13 Sep 2010
- Mikdash-Shamailov, Liya (2002). Mountain Jews - Customs and Daily Life in the Caucasus (Softcover). Jerusalem: The Israel Museum. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Tolts, Mark (22 October 2007). "Demography of North Caucasian Jewry: A note on population dynamics and shifting identity". In Gammer, Moshe (ed.). Ethno-Nationalism, Islam and the State in the Caucasus (1 ed.). Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203933794. ISBN 9780203933794. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Enoch, Reuven; Lomtadze, Tamari (19 June 2019). "Judeo-Georgian Language as an Identity Marker of Georgian Jews (The Jews Living in Georgia)". Journal of Jewish Languages. Brill. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Lomtadze, Tamari; Guledani, Lali (22 October 2024). "The Geographical and Social Stratification of Judeo-Georgian". Journal of Jewish Languages. 12 (2): 125–146. doi:10.1163/22134638-bja10053. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Gitelman, Zvi (1991). "Ethnic identity and ethnic relations among the Jews of the non-European USSR". Ethnic and Racial Studies. 14 (1: National identity in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union): 24–54. doi:10.1080/01419870.1991.9993697. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑
- Peacock, A.C.S. (2011). "Identity, Culture and Religion on Medieval Islam's Caucasian Frontier" (PDF). Bulletin of the Royal Institute for Inter-Faith Studies. 13: 69–90. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Gelovani, Nani (January 2013). "Arab-Byzantine Relations under the Umayyad Caliphate and South Caucasus". International Journal of Social Science and Humanity (IJSSH). 3 (1). Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Djaparidze, Gotcha; Gelovani, Nani (2018). "The Muslim subjects of the kingdom of Georgia in the 12th-early 13th century" (PDF). Journal of Advances in Humanities and Social Sciences (JAHSS). 4 (4): 161–166. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Kiknadze, Vazha (2020). "East-West cultural dialogue in Georgia during the Queen Tamar's Reign". Tyragetia (Serie Nouă) (2). Muzeul Naţional de Istorie a Moldovei: 57–62. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- Vacca, Alison M. "Chapter 2: The Armenian Sources of al-Balādhurī's Kitāb Futūḥ al-buldān: A Study of the Islamic Incursions into Armenia, Georgia, and Albania (22–24 AH/642–645 CE)". Islam on the Margins. Brill. pp. 20–46. doi:10.1163/9789004527836_003. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ↑ "Lari". საქართველოს ეროვნული ბანკი (National Bank of Georgia). Retrieved 2 December 2024.